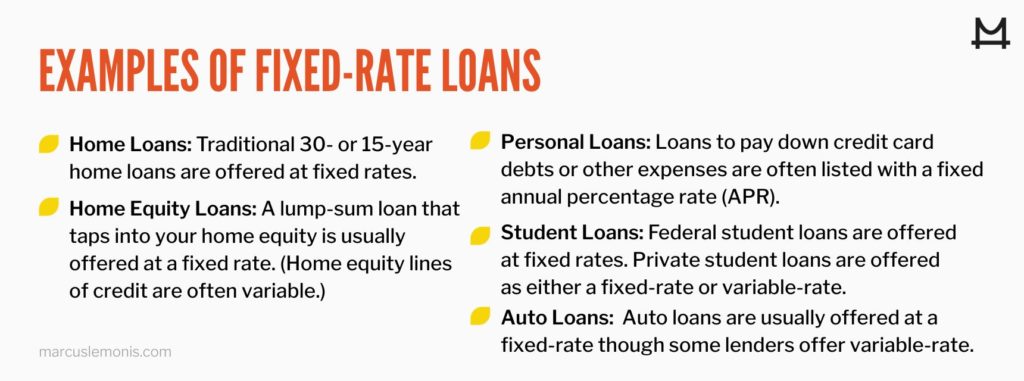
What Kind of Loan Do You Need?
A fixed-rate loan for a car purchase or a mortgage for your home has an interest rate that will not change through the duration of the loan. For instance, if you secure an interest rate of 6.5% for a 30-year mortgage, your principal and interest payment will be roughly the same from the first payment to the last. This generally applies to personal loans; if you are in the market for a business loan, there are several different business lines of credit to consider.

Variable rate loans, such as you may be offered in a home equity line of credit or other type of mortgage, can rise and fall depending on benchmark interest rates or indexes that change with the market. The type of loan and what rate it is tied to varies, but generally, a variable rate loan will depend on the federal funds rate or the London Inter-Bank Offered Rate (or LIBOR). In June 2023, the Secured Overnight Financing Rate is the benchmark that will replace LIBOR, which is being phased out.
A fixed-rate loan is not subject to these benchmarks and will not fluctuate, but your monthly payment may change depending on the taxes and insurance that are added to your mortgage payment.
How a Fixed-Rate Loan Works
A lender sets the fixed interest rate when issuing your loan. The lender will likely consider many factors, including your income, credit rating, current assets, the size of the down payment you can make, as well as personal factors such as whether you’re a veteran or if you’ve previously filed for bankruptcy.

For instance, if you have a good credit history and a credit score above 740, which is the baseline for a very good score, you will be offered a rate that is lower than if your credit score was 650, or fair.
Once you are approved for the loan, say for a 30-year fixed $500,000 mortgage using the example above of a 6.5% interest rate, you would pay $3,160 per month, plus insurance and taxes. If your circumstances and background cause the lender to offer a higher rate of 7.1%, your monthly payment—again, minus insurance and taxes—rises to $3,360, or $200 more per month. In other words, even small fluctuations in interest rates have a significant effect; $200 monthly for 30 years equates to $72,000!

Why Choose a Fixed-Rate Rather Than Variable-Rate Loan?
The primary reason to select a fixed-rate loan over a variable-rate loan is stability. If interest rates rise, the amount you pay stays the same.
Reasons to opt for variable-rate loans include the allure of a lower interest rate, though that can be risky. When interest rates rise, as they have at the end of 2022, the loan terms become less palatable—and more expensive. Another reason to to opt for a variable-rate loan is if it is offered at a lower interest rate than a fixed loan, and you are certain you will be able to pay the loan off quickly.

- When selecting home, auto, or other loans, should you choose a fixed-rate or variable loan?
- How much will you pay in interest over the life of the loan?